Usage
Introduction
To debug with LaraDumps, simply add a ds() in your code.
It's quite similar to using the dump() or dd() functions, but with the benefit of seeing your debug dump in a dedicated Desktop Application.
Try it yourself
Add the ds() function to your routes/web.php main route, just like in the code below:
// File: routes/web.php
Route::get('/', function () {
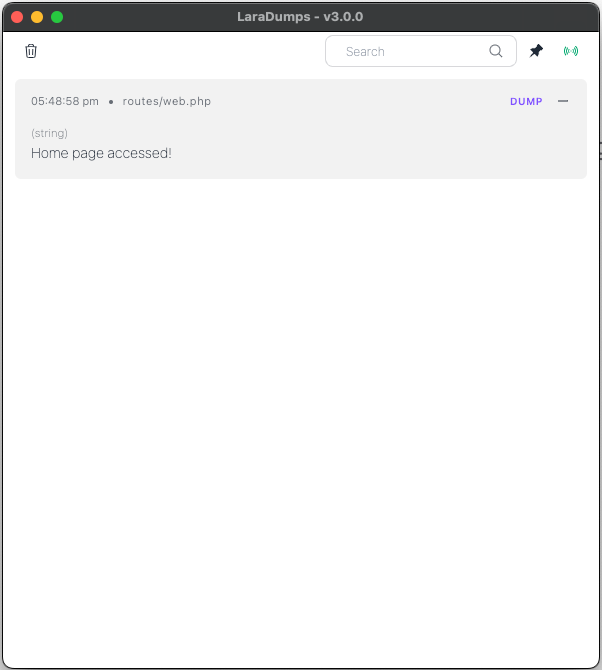
ds('Home page accessed!'); //<==========
return view('home');
});Now, access your home-page, and you will see the debug dump in the Desktop App:
TIP
💡 Trivia: The "ds()" function is based on the first and last letters of the word dumps, and it is conveniently similar to "dd()". This is not a coincidence! Easy to switch!
Debug Tools
LaraDumps provides you with a set of tools to debug your code and inspect what is happening to your application during the development process.
Dump
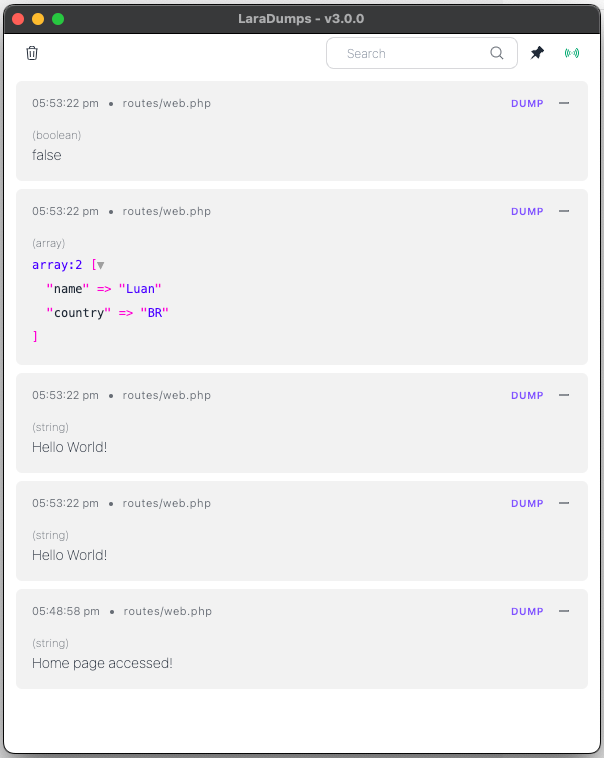
To send a dump to the application, just pass one or more values to the ds() function.
$myString = 'Hello World!';
$myArray = ['name' => 'Luan', 'country' => 'BR'];
$myBoolean = false;
//Single value
ds($myString);
//Multiple values
ds($myString, $myArray, $myBoolean);This function is similar to Laravel's dump() and it will not stop the code execution.
Dump and die
Use the function ds()->die() or its shortcut dsd() to dump and immediately stop the code execution.
$myString = 'Hello World!';
ds($myString)->die();
//dsd($myString);
ds('This will never happen');This function is similar to Laravel's dd().
Quiet dump
By default, LaraDumps Desktop App will be invoked and gain focus whenever a new dump is received.
If this is not what you want, simply disable the Auto-Invoke feature.
Alternatively, just use the dsq() method and send a quiet dump. This will not invoke the App.
// Requires Auto-Invoke to be enabled
$products = [['id' => 1, 'price' => 10], ['id' => 2, 'price' => 50], ['id' => 3, 'price' => -5]];
foreach ($products as $product) {
dsq('Checking product #' . $product['id']); //Send a dump without invoking the app
if ($product['price'] < 0) {
ds('Price error in product #' . $product['id']); //App will be invoked
}
}The previous example will quietly dump each product prices and only invoke in case the price is invalid.
Label
You can use the label() method to set a label to your debug dump.
Assigning a label makes it easier to locate the debug dump among other similar results.
$person = ['name' => 'Luan', 'country' => 'BR'];
$person2 = ['name' => 'Taylor', 'country' => 'US'];
ds($person)->label('Creator of Laradumps');
ds($person2)->label('Creator of Laravel');Screens
You can use the toScreen() or s() methods to send your debug dump to a specific Screen.
By opening different screens, you can better organize your dumps into groups of similar issues.
ds('this is screen 1'); //default screen
ds('this is screen 2')->toScreen('screen 2');
ds('custom value')->s('Custom screen');Clear Screens
You can use the clear() method to delete all previous dumps from all screens.
This will reset your application to the start point.
ds()->clear();TIP
📝 Note: To clear only the current screen, click on the × at the right end of the screen list.
Color Tag
You can use the color() method to mark a dump with a predefined color.
ds('Info: Just FYI')->info(); // or ->blue()
ds('Success: IT WORKS!')->success(); // or ->green()
ds('Danger: ERROR!!!')->danger(); // or ->red()
ds('Warning: Something is not right!')->warning(); // or ->orange()
ds('Dark: The Dark Side of the Moon')->dark(); // or ->black()Time
To simply measure the execution time of a block of code, place it within the time($reference) and stopTime($reference) methods.
You must pass the same unique $reference title to both methods. The reference can be any combination of words.
ds()->time('my count');
for($i=0; $i<100000; $i++){
//some code
}
ds()->stopTime('my count');Model Inspection
- Only available for laradumps/laradumps
You can use the model() method to view Eloquent Model's Attributes and Relationships.
use App\Models\User;
$firstUser = User::first();
ds()->model($firstUser);Table
You can use the table() method to display dumps in a table with a built-in search bar.
To build a table, you must pass an iterable $data as the first argument, followed by an optional string $name for the table name.
use App\Models\User;
// Using an iterable
$allUsers = [
['id' => 1, 'name' => 'David', 'email' => 'david@example.com'],
['id' => 2, 'name' => 'Julia', 'email' => 'julia@example.com'],
//...
];
// Using Eloquent
$allUsers = User::all(['id', 'name', 'email']);
ds()->table($allUsers, 'my users table');JSON
Use the isJson() method to validate and display JSON strings in human-readable format.
This is very helpful for checking JSON content sent from an API or front-end app.
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
// Json from API
$moviesJson = Http::get('https://api.tvmaze.com/search/people?q=lauren')->body();
ds($moviesJson)->isJson();
//Invalid JSON
ds('{"name: Luan}')->isJson();Contains
You can use the contains() method to verify if a given string appears in the dump.
This is particularly useful when working with longer strings that require a lot of time to inspect and debug.
$html = '<select name="select-choice" id="select-choice"><option value="Choice 1">Choice 1</option><option value="Choice 2">Choice 2</option><option value="Choice 3">Choice 3</option></select>';
ds($html)->contains('Choice 3')->label('Must be there');
ds($html)->contains('Choice 29')->label('Should not contain');For a stricter search, you can activate Case Sensitive or Whole word parameters:
$json = '{"name":"Mariana", "country":"Brazil"}';
//Will not match "Brazil"
ds($json)->contains('brazil', caseSensitive: true);
//No match for "Maria" in "Mariana"
ds($json)->contains('Maria', wholeWord: true);Markdown
- Only available for laradumps/laradumps
Displays the markdown rendered as HTML.
ds()->markdown('# Hi, Anand Pilania!');PHPInfo
Displays the current PHP settings in table format.
ds()->phpinfo();Benchmark
Benchmark closures (array of closures or a variable number of closures as arguments) and dump detailed results including start time, end time, total execution time, and result for each closure and also includes a fastest flag to indicate the fastest closure in the results.
ds()->benchmark(
function() {
sleep(2);
return 'First';
},
function(){
sleep(1);
return 'Second';
}
);You can also add custom labels for each closures:
ds()->benchmark([
'Label 1' => function() {
sleep(1);
return 'Result 1';
},
'Label 2' => function() {
sleep(2);
return 'Result 2';
},
]);You can also chain multiple benchmarks or other tools:
ds()->benchmark(
...
)->benchmark(
...
)->table(..., ...);